淺談LLDB調試器
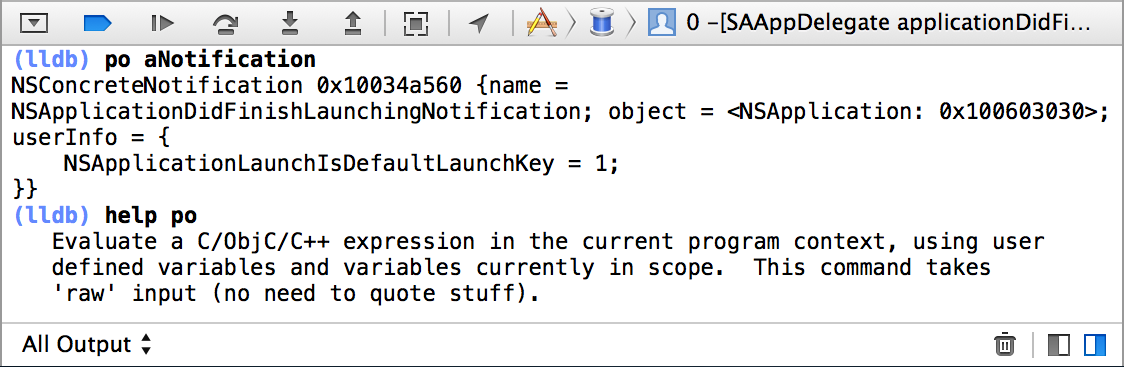
隨著Xcode 5的發布,LLDB調試器已經取代了GDB,成為了Xcode工程中默認的調試器。它與LLVM編譯器一起,帶給我們更豐富的流程控制和數據檢測的調試功能。LLDB為Xcode提供了底層調試環境,其中包括內嵌在Xcode IDE中的位於調試區域的控制面板,在這裡我們可以直接調用LLDB命令。如圖1所示:
圖1:位於Xcode調試區域的控制台
在本文中,我們主要整理一下LLDB調試器提供給我們的調試命令,更詳細的內容可以查看The LLDB Debugger。
LLDB命令結構
在使用LLDB前,我們需要了解一下LLDB的命令結構及語法,這樣可以盡可能地挖掘LLDB的潛能,以幫助我們更充分地利用它。
LLDB命令的語法有其通用結構,通常是以下形式的:
[ [ ...]] [-options [option-value]] [argument [argument...]]
其中:
:我們想在前面的命令序列的上下文中執行的一些操作。
:根據使用的命令的上下文來表示各種不同的東西。
LLBD命令行的解析操作在執行命令之前完成。上面的這些元素之間通過空格來分割,如果某一元素自身含有空格,則可以使用雙引用。而如果元素中又包含雙引號,則可以使用反斜槓;或者元素使用單引號。如下所示:
(lldb) command [subcommand] -option "some \"quoted\" string" (lldb) command [subcommand] -option 'some "quoted" string'
這種命令解析設計規范了LLDB命令語法,並對所有命令做了個統一。
命令選項
LLDB中的命令選項有規范形式和縮寫形式兩種格式。以設置斷點的命令breakpoint set為例,以下列表了其部分選項的格式,其中括號中的是規范形式:
breakpoint set -M( --method ) -S ( --selector ) -b ( --basename ) -f ( --file ) -l ( --line ) -n ( --name ) …
各選項的順序是任意的。如果後面的參數是以”–“開頭的,則在選項後面添加”—“作為選項的終止信號,以告訴LLDB我們處理的選項的正確位置。如下命令所示:
(lldb) process launch --stop-at-entry -- -program_arg_1 value -program_arg_2 value
如上所示,命令的選項是—stop-at-entry,參數是-program_arg_1和-program_arg_2,我們使用”—“將選項與參數作一下區分。
原始命令
LLDB命令解析器支持”原始(raw)“命令,即沒有命令選項,命令字符串的剩余部分未經解析就傳遞給命令。例如,expression就是一個原始命令。
不過原始命令也可以有選項,如果命令字符串中有虛線,則在命令名與命令字符串之間放置一個選項結束符(—)來表明沒有命令標記。
我們可以通過help命令的輸出來查看一個命令是否是原始命令。
命令補全(Command Completion)
LLDB支持源文件名,符號名,文件名,等等的命令補全(Commmand Completion)。終端窗口中的補全是通過在命令行中輸入一個制表符來初始化的。Xcode控制台中的補全與在源碼編輯器中的補全方式是一樣的:補全會在第三個字符被鍵入時自動彈出,或者通過Esc鍵手動彈出。
一個命令中的私有選項可以有不同的完成者(completers)。如breakpoint中的—file 選項作為源文件的完成者,—shlib 選項作為當前加載的庫的完成者,等等。這些行為是特定的,例如,如果指定—shlib ,且以—file 結尾,則LLDB只會列出由—shlib 指定的共享類庫。
Python腳本
對於高級用戶來說,LLDB有一個內置的Python解析器,可以通過腳本命令來訪問。調試器中的所有特性在Python解析器中都可以作為類來訪問。這樣,我們就可以使用LLDB-Python庫來寫Python函數,並通過腳本將其加載到運行會話中,以執行一些更復雜的調試操作。
在命令行中調試程序
通常我們都是在Xcode中直接使用LLDB調試器,Xcode會幫我們完成很多操作。當然,如果我們想讓自己看著更Bigger,或者想了解下調試器具體的一些流程,就可以試試直接在終端使用LLDB命令來調試程序。在終端中使用LLDB調試器,我們需要了解以下內容:
1.加載程序以備調試
2.將一個運行的程序綁定到LLDB
3.設置斷點和觀察點
4.控制程序的執行
5.在調試的程序中導航
6.檢查狀態和值的變量
7.執行替代代碼
了解在終端中這些操作是如何進行的,可以幫助我們更深入的了解調試器在Xcode中是如何運作的。下面我們分步來介紹一下。
指定需要調試的程序
首先我們需要設置需要調試的程序。我們可以使用如下命令做到這一點:
$ lldb /Projects/Sketch/build/Debug/Sketch.app Current executable set to '/Projects/Sketch/build/Debug/Sketch.app' (x86_64).
或者在運行lldb後,使用file命令來處理,如下所示:
$ lldb (lldb) file /Projects/Sketch/build/Debug/Sketch.app Current executable set to '/Projects/Sketch/build/Debug/Sketch.app' (x86_64).
設置斷點
在設置完程序後,我們可能想設置一點斷點來調試程序。此時我們可以使用breakpoint set命令來設置斷點,這個命令簡單、直觀,且有智能補全,接下來我們看看它的具體操作。
如果想在某個文件中的某行設置一個斷點,可使用以下命令:
(lldb) breakpoint set --file foo.c --line 12
如果想給某個函數設置斷點,可使用以下命令:
(lldb) breakpoint set --name foo
如果想給C++中所有命名為foo的方法設置斷點,可以使用以下命令:
(lldb) breakpoint set --method foo
如果想給Objective-C中所有命名為alignLeftEdges:的選擇器設置斷點,則可以使用以下命令:
(lldb) breakpoint set --selector alignLeftEdges:
我們可以使用—shlib
(lldb) breakpoint set --shlib foo.dylib --name foo
看吧,斷點設置命令還是很強大的。
如果我們想查看程序中所有的斷點,則可以使用breakpoint list命令,如下所示:
(lldb) breakpoint list Current breakpoints: 1: name = 'alignLeftEdges:', locations = 1, resolved = 1 1.1: where = Sketch`-[SKTGraphicView alignLeftEdges:] + 33 at /Projects/Sketch/SKTGraphicView.m:1405, address = 0x0000000100010d5b, resolved, hit count = 0
從上面的輸出結果可以看出,一個斷點一般有兩部分:
1.斷點的邏輯規范,這一部分是用戶提供給breakpoint set命令的。
2.與規范匹配的斷點的位置。
如上所示,通過”breakpoint set —selector alignLeftEdges:“設置的斷點,其信息中會顯示出所有alignLeftEdges:方法的位置。
breakpoint list命令輸出列表顯示每個邏輯斷點都有一個整數標識,如上所示斷點標識為1。而每個位置也會有一個標識,如上所示的1.1。
輸出列表中另一個信息是斷點位置是否是已解析的(resolved)。這個標識表示當與之相關的文件地址被加載到程序進行調試時,其位置是已解析的。例如,如果在共享庫中設置的斷點之後被卸載了,則斷點的位置還會保留,但其不能再被解析。
不管是邏輯斷點產生的所有位置,還是邏輯斷點解析的任何特定位置,我們都可以使用斷點觸發命令來對其進行刪除、禁用、設置條件或忽略計數操作。例如,如果我們想添加一個命令,以在LLDB命中斷點1.1時打印跟蹤棧,則可以執行以下命令
(lldb) breakpoint command add 1.1 Enter your debugger command(s). Type 'DONE' to end. > bt > DONE
如果想更詳細地了解”breakpoint command add”命令的使用,可以使用help幫助系統來查看。
設置觀察點
作為斷點的補充,LLDB支持觀察點以在不中斷程序運行的情況下監測一些變量。例如,我們可以使用以下命令來監測名為global的變量的寫操作,並在(global==5)為真時停止監測:
(lldb) watch set var global
Watchpoint created: Watchpoint 1: addr = 0x100001018 size = 4 state = enabled type = w
declare @ '/Volumes/data/lldb/svn/ToT/test/functionalities/watchpoint/watchpoint_commands/condition/main.cpp:12'
(lldb) watch modify -c '(global==5)'
(lldb) watch list
Current watchpoints:
Watchpoint 1: addr = 0x100001018 size = 4 state = enabled type = w
declare @ '/Volumes/data/lldb/svn/ToT/test/functionalities/watchpoint/watchpoint_commands/condition/main.cpp:12'
condition = '(global==5)'
(lldb) c
Process 15562 resuming
(lldb) about to write to 'global'...
Process 15562 stopped and was programmatically restarted.
Process 15562 stopped and was programmatically restarted.
Process 15562 stopped and was programmatically restarted.
Process 15562 stopped and was programmatically restarted.
Process 15562 stopped
* thread #1: tid = 0x1c03, 0x0000000100000ef5 a.out`modify + 21 at main.cpp:16, stop reason = watchpoint 1
frame #0: 0x0000000100000ef5 a.out`modify + 21 at main.cpp:16
13
14 static void modify(int32_t &var) {
15 ++var;
-> 16 }
17
18 int main(int argc, char** argv) {
19 int local = 0;
(lldb) bt
* thread #1: tid = 0x1c03, 0x0000000100000ef5 a.out`modify + 21 at main.cpp:16, stop reason = watchpoint 1
frame #0: 0x0000000100000ef5 a.out`modify + 21 at main.cpp:16
frame #1: 0x0000000100000eac a.out`main + 108 at main.cpp:25
frame #2: 0x00007fff8ac9c7e1 libdyld.dylib`start + 1
(lldb) frame var global
(int32_t) global = 5
(lldb) watch list -v
Current watchpoints:
Watchpoint 1: addr = 0x100001018 size = 4 state = enabled type = w
declare @ '/Volumes/data/lldb/svn/ToT/test/functionalities/watchpoint/watchpoint_commands/condition/main.cpp:12'
condition = '(global==5)'
hw_index = 0 hit_count = 5 ignore_count = 0
(lldb)可以使用help watchpoint來查看該命令的使用。
使用LLDB來啟動程序
一旦指定了調試哪個程序,並為其設置了一些斷點後,就可以開始運行程序了。我們可以使用以下命令來啟動程序:
(lldb) process launch (lldb) run (lldb) r
我們同樣可以使用進程ID或進程名來連接一個已經運行的程序。當使用名稱來連接一個程序時,LLDB支持—waitfor選項。這個選項告訴LLDB等待下一個名稱為指定名稱的程序出現,然後連接它。例如,下面3個命令都是用於連接Sketch程序(假定其進程ID為123):
(lldb) process attach --pid 123 (lldb) process attach --name Sketch (lldb) process attach --name Sketch --waitfor
啟動或連接程序後,進程可能由於某些原因而停止,如:
(lldb) process attach -p 12345 Process 46915 Attaching Process 46915 Stopped 1 of 3 threads stopped with reasons: * thread #1: tid = 0x2c03, 0x00007fff85cac76a, where = libSystem.B.dylib`__getdirentries64 + 10, stop reason = signal = SIGSTOP, queue = com.apple.main-thread
注意“1 of 3 threads stopped with reasons:”及其下面一行。在多線程環境下,在內核實際返回控制權給調試器前,可能會有多個線程命中同一個斷點。在這種情況下,我們可以在停止信息中看到所有因此而停止的線程。
控制程序
啟動程序後,LLDB允許程序在到達斷點前繼續運行。LLDB中流程控制的命令都在thread命令層級中。如下所示:
(lldb) thread continue Resuming thread 0x2c03 in process 46915 Resuming process 46915
另外,還有以下命令:
(lldb) thread step-in // The same as "step" or "s" in GDB. (lldb) thread step-over // The same as "next" or "n" in GDB. (lldb) thread step-out // The same as "finish" or "f" in GDB. (lldb) thread step-inst // The same as "stepi" / "si" in GDB. (lldb) thread step-over-inst // The same as "nexti" / "ni" in GDB.
LLDB還提供了run until line按步調度模式,如:
lldb) thread until 100
這條命令會運行線程,直到當前frame到達100行。如果代碼在運行的過程中跳過了100行,則當frame被彈出棧後終止執行。
查看線程狀態
在進程停止後,LLDB會選擇一個當前線程和線程中當前幀(frame)。很多檢測狀態的命令可以用於這個線程或幀。
為了檢測進程的當前狀態,可以從以下命令開始:
(lldb) thread list Process 46915 state is Stopped * thread #1: tid = 0x2c03, 0x00007fff85cac76a, where = libSystem.B.dylib`__getdirentries64 + 10, stop reason = signal = SIGSTOP, queue = com.apple.main-thread thread #2: tid = 0x2e03, 0x00007fff85cbb08a, where = libSystem.B.dylib`kevent + 10, queue = com.apple.libdispatch-manager thread #3: tid = 0x2f03, 0x00007fff85cbbeaa, where = libSystem.B.dylib`__workq_kernreturn + 10
星號(*)表示thread #1為當前線程。為了獲取線程的跟蹤棧,可以使用以下命令:
(lldb) thread backtrace thread #1: tid = 0x2c03, stop reason = breakpoint 1.1, queue = com.apple.main-thread frame #0: 0x0000000100010d5b, where = Sketch`-[SKTGraphicView alignLeftEdges:] + 33 at /Projects/Sketch/SKTGraphicView.m:1405 frame #1: 0x00007fff8602d152, where = AppKit`-[NSApplication sendAction:to:from:] + 95 frame #2: 0x00007fff860516be, where = AppKit`-[NSMenuItem _corePerformAction] + 365 frame #3: 0x00007fff86051428, where = AppKit`-[NSCarbonMenuImpl performActionWithHighlightingForItemAtIndex:] + 121 frame #4: 0x00007fff860370c1, where = AppKit`-[NSMenu performKeyEquivalent:] + 272 frame #5: 0x00007fff86035e69, where = AppKit`-[NSApplication _handleKeyEquivalent:] + 559 frame #6: 0x00007fff85f06aa1, where = AppKit`-[NSApplication sendEvent:] + 3630 frame #7: 0x00007fff85e9d922, where = AppKit`-[NSApplication run] + 474 frame #8: 0x00007fff85e965f8, where = AppKit`NSApplicationMain + 364 frame #9: 0x0000000100015ae3, where = Sketch`main + 33 at /Projects/Sketch/SKTMain.m:11 frame #10: 0x0000000100000f20, where = Sketch`start + 52
如果想查看所有線程的調用棧,則可以使用以下命令:
(lldb) thread backtrace all
查看調用棧狀態
檢查幀參數和本地變量的最簡便的方式是使用frame variable命令:
(lldb) frame variable self = (SKTGraphicView *) 0x0000000100208b40 _cmd = (struct objc_selector *) 0x000000010001bae1 sender = (id) 0x00000001001264e0 selection = (NSArray *) 0x00000001001264e0 i = (NSUInteger) 0x00000001001264e0 c = (NSUInteger) 0x00000001001253b0
如果沒有指定任何變量名,則會顯示所有參數和本地變量。如果指定參數名或變量名,則只打印指定的值。如:
(lldb) frame variable self (SKTGraphicView *) self = 0x0000000100208b40
frame variable命令不是一個完全的表達式解析器,但它支持一些簡單的操作符,如&,*,–>,[]。這個數組括號可用於指針,以將指針作為數組處理。如下所示:
(lldb) frame variable *self
(SKTGraphicView *) self = 0x0000000100208b40
(NSView) NSView = {
(NSResponder) NSResponder = {
...
(lldb) frame variable &self
(SKTGraphicView **) &self = 0x0000000100304ab
(lldb) frame variable argv[0]
(char const *) argv[0] = 0x00007fff5fbffaf8 "/Projects/Sketch/build/Debug/Sketch.app/Contents/MacOS/Sketch"frame variable命令會在變量上執行”對象打印”操作。目前,LLDB只支持Objective-C打印,使用的是對象的description方法。
如果想查看另外一幀,可以使用frame select命令,如下所示:
(lldb) frame select 9 frame #9: 0x0000000100015ae3, where = Sketch`function1 + 33 at /Projects/Sketch/SKTFunctions.m:11
小結
以上所介紹的命令可以讓我們在終端中直接調試程序。當然,很多命令也可以在Xcode中直接使用。這些命令可以讓我們了解程序運行的狀態,當然有些狀態可以在Xcode中了解到。建議在調試過程中,可以多使用這些命令。
如果想了解這一過程中使用的各種命令,可以查看蘋果的官方文檔。
在Xcode中調試程序
對於我們日常的開發工作來說,更多的時候是在Xcode中進行調試工作。因此上面所描述的流程,其實Xcode已經幫我們完成了大部分的工作,而且很多東西也可以在Xcode裡面看到。因此,我們可以把精力都集中在代碼層面上。
在蘋果的官方文檔中列出了我們在調試中能用到的一些命令,我們在這重點講一些常用的命令。
打印
打印變量的值可以使用print命令,該命令如果打印的是簡單類型,則會列出簡單類型的類型和值。如果是對象,還會打印出對象指針地址,如下所示:
(lldb) print a (NSInteger) $0 = 0 (lldb) print b (NSInteger) $1 = 0 (lldb) print str (NSString *) $2 = 0x0000000100001048 @"abc" (lldb) print url (NSURL *) $3 = 0x0000000100206cc0 @"abc"
在輸出結果中我們還能看到類似於$0,$1這樣的符號,我們可以將其看作是指向對象的一個引用,我們在控制面板中可以直接使用這個符號來操作對應的對象,這些東西存在於LLDB的全名空間中,目的是為了輔助調試。如下所示:
(lldb) exp $0 = 100 (NSInteger) $9 = 100 (lldb) p a (NSInteger) $10 = 100
另外$後面的數值是遞增的,每打印一個與對象相關的命令,這個值都會加1。
上面的print命令會打印出對象的很多信息,如果我們只想查看對象的值的信息,則可以使用po(print object的縮寫)命令,如下所示:
(lldb) po str abc
當然,po命令是”exp -O —“命令的別名,使用”exp -O —”能達到同樣的效果。
對於簡單類型,我們還可以為其指定不同的打印格式,其命令格式是print/,如下所示:
(lldb) p/x a (NSInteger) $13 = 0x0000000000000064
格式的完整清單可以參考Output Formats。
expression
在開發中,我們經常會遇到這樣一種情況:我們設置一個視圖的背景顏色,運行後發現顏色不好看。嗯,好吧,在代碼裡面修改一下,再編譯運行一下,嗯,還是不好看,然後再修改吧~~這樣無形中浪費了我們大把的時間。在這種情況下,expression命令強大的功能就能體現出來了,它不僅會改變調試器中的值,還改變了程序中的實際值。我們先來看看實際效果,如下所示:
(lldb) exp a = 10 (NSInteger) $0 = 10 (lldb) exp b = 100 (NSInteger) $1 = 100 2015-01-25 14:00:41.313 test[18064:71466] a + b = 110, abc
expression命令的功能不僅於此,正如上面的po命令,其實際也是”expression -O —“命令的別名。更詳細使用可以參考Evaluating Expressions。
image
image命令的用法也挺多,首先可以用它來查看工程中使用的庫,如下所示:
(lldb) image list [ 0] 432A6EBF-B9D2-3850-BCB2-821B9E62B1E0 0x0000000100000000 /Users/**/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/test-byjqwkhxixddxudlnvqhrfughkra/Build/Products/Debug/test [ 1] 65DCCB06-339C-3E25-9702-600A28291D0E 0x00007fff5fc00000 /usr/lib/dyld [ 2] E3746EDD-DFB1-3ECB-88ED-A91AC0EF3AAA 0x00007fff8d324000 /System/Library/Frameworks/Foundation.framework/Versions/C/Foundation [ 3] 759E155D-BC42-3D4E-869B-6F57D477177C 0x00007fff8869f000 /usr/lib/libobjc.A.dylib [ 4] 5C161F1A-93BA-3221-A31D-F86222005B1B 0x00007fff8c75c000 /usr/lib/libSystem.B.dylib [ 5] CBD1591C-405E-376E-87E9-B264610EBF49 0x00007fff8df0d000 /System/Library/Frameworks/CoreFoundation.framework/Versions/A/CoreFoundation [ 6] A260789B-D4D8-316A-9490-254767B8A5F1 0x00007fff8de36000 /usr/lib/libauto.dylib ......
我們還可以用它來查找可執行文件或共享庫的原始地址,這一點還是很有用的,當我們的程序崩潰時,我們可以使用這條命令來查找崩潰所在的具體位置,如下所示:
NSArray *array = @[@1, @2]; NSLog(@"item 3: %@", array[2]);
這段代碼在運行後會拋出如下異常:
2015-01-25 14:12:01.007 test[18122:76474] *** Terminating app due to uncaught exception 'NSRangeException', reason: '*** -[__NSArrayI objectAtIndex:]: index 2 beyond bounds [0 .. 1]' *** First throw call stack: ( 0 CoreFoundation 0x00007fff8e06f66c __exceptionPreprocess + 172 1 libobjc.A.dylib 0x00007fff886ad76e objc_exception_throw + 43 2 CoreFoundation 0x00007fff8df487de -[__NSArrayI objectAtIndex:] + 190 3 test 0x0000000100000de0 main + 384 4 libdyld.dylib 0x00007fff8f1b65c9 start + 1 ) libc++abi.dylib: terminating with uncaught exception of type NSException
根據以上信息,我們可以判斷崩潰位置是在main.m文件中,要想知道具體在哪一行,可以使用以下命令:
(lldb) image lookup --address 0x0000000100000de0 Address: test[0x0000000100000de0] (test.__TEXT.__text + 384) Summary: test`main + 384 at main.m:23
可以看到,最後定位到了main.m文件的第23行,正是我們代碼所在的位置。
我們還可以使用image lookup命令來查看具體的類型,如下所示:
(lldb) image lookup --type NSURL
Best match found in /Users/**/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/test-byjqwkhxixddxudlnvqhrfughkra/Build/Products/Debug/test:
id = {0x100000157}, name = "NSURL", byte-size = 40, decl = NSURL.h:17, clang_type = "@interface NSURL : NSObject{
NSString * _urlString;
NSURL * _baseURL;
void * _clients;
void * _reserved;
}
@property ( readonly,getter = absoluteString,setter = ,nonatomic ) NSString * absoluteString;
@property ( readonly,getter = relativeString,setter = ,nonatomic ) NSString * relativeString;
@property ( readonly,getter = baseURL,setter = ,nonatomic ) NSURL * baseURL;
@property ( readonly,getter = absoluteURL,setter = ,nonatomic ) NSURL * absoluteURL;
@property ( readonly,getter = scheme,setter = ,nonatomic ) NSString * scheme;
@property ( readonly,getter = resourceSpecifier,setter = ,nonatomic ) NSString * resourceSpecifier;
@property ( readonly,getter = host,setter = ,nonatomic ) NSString * host;
@property ( readonly,getter = port,setter = ,nonatomic ) NSNumber * port;
@property ( readonly,getter = user,setter = ,nonatomic ) NSString * user;
@property ( readonly,getter = password,setter = ,nonatomic ) NSString * password;
@property ( readonly,getter = path,setter = ,nonatomic ) NSString * path;
@property ( readonly,getter = fragment,setter = ,nonatomic ) NSString * fragment;
@property ( readonly,getter = parameterString,setter = ,nonatomic ) NSString * parameterString;
@property ( readonly,getter = query,setter = ,nonatomic ) NSString * query;
@property ( readonly,getter = relativePath,setter = ,nonatomic ) NSString * relativePath;
@property ( readonly,getter = fileSystemRepresentation,setter = ) const char * fileSystemRepresentation;
@property ( readonly,getter = isFileURL,setter = ,readwrite ) BOOL fileURL;
@property ( readonly,getter = standardizedURL,setter = ,nonatomic ) NSURL * standardizedURL;
@property ( readonly,getter = filePathURL,setter = ,nonatomic ) NSURL * filePathURL;
@end" 可以看到,輸出結果中列出了NSURL的一些成員變量及屬性信息。
image命令還有許多其它功能,具體可以參考Executable and Shared Library Query Commands。
流程控制
流程控制的命令實際上我們在上一小節已經講過了,在Xcode的控制面板中同樣可以使用這些命令,在此不在重復。
命令別名及幫助系統
LLDB有兩個非常有用的特性,即命令別名及幫助。
命令別名
我們可以使用LLDB的別名機制來為常用的命令創建一個別名,以方便我們的使用,如下命令:
(lldb) breakpoint set --file foo.c --line 12
如果在我們的調試中需要經常用到這條命令,則每次輸入這麼一長串的字符一定會很讓人抓狂。此時,我們就可以為這條命令創建一個別名,如下所示:
(lldb) command alias bfl breakpoint set -f %1 -l %2
這樣,我們只需要按如下方式來使用它即可:
(lldb) bfl foo.c 12
是不是簡單多了?
我們可以自由地創建LLDB命令的別名集合。LLDB在啟動時會讀取~/.lldbinit文件。這個文件中存儲了command alias命令創建的別名。LLDB幫助系統會讀取這個初始化文件並會列出這些別名,以讓我們了解自己所設置的別名。我們可以使用”help -a”命令並在輸出的後面來查看這邊別名,其以下面這行開始:
... The following is a list of your current command abbreviations (see 'help command alias' for more info): ...
如果我們不喜歡已有命令的別名,則可以使用以下命令來取消這個別名:
(lldb) command unalias b
幫助系統
LLDB幫助系統讓我們可以了解LLDB提供了哪些功能,並可以查看LLDB命令結構的詳細信息。熟悉幫助系統可以讓我們訪問幫助系統中中命令文檔。
我們可以簡單地調用help命令來列出LLDB所有的頂層命令。如下所示:
(lldb) help The following is a list of built-in, permanent debugger commands: _regexp-attach -- Attach to a process id if in decimal, otherwise treat the argument as a process name to attach to. _regexp-break -- Set a breakpoint using a regular expression to specify the location, whereis in decimal and is in hex. _regexp-bt -- Show a backtrace. An optional argument is accepted; if that argument is a number, it specifies the number of frames to display. If that argument is 'all', full backtraces of all threads are displayed. … and so forth …
如果help後面跟著某個特定的命令,則會列出該命令相關的所有信息,我們以breakpoint set為例,輸出信息如下:
(lldb) help breakpoint set Sets a breakpoint or set of breakpoints in the executable. Syntax: breakpoint setCommand Options Usage: breakpoint set [-Ho] -l [-s ] [-i ] [-c ] [-x ] [-t ] [-T ] [-q ] [-f ] [-K ] breakpoint set [-Ho] -a [-s ] [-i ] [-c ] [-x ] [-t ] [-T ] [-q ] breakpoint set [-Ho] -n [-s ] [-i ] [-c ] [-x ] [-t ] [-T ] [-q ] [-f ] [-K ] [-L ] breakpoint set [-Ho] -F [-s ] [-i ] [-c ] [-x ] [-t ] [-T ] [-q ] [-f ] [-K ] … and so forth …
還有一種更直接的方式來查看LLDB有哪些功能,即使用apropos命令:它會根據關鍵字來搜索LLDB幫助文檔,並為每個命令選取一個幫助字符串,我們以apropos file為例,其輸出如下:
(lldb) apropos file The following commands may relate to 'file': … log enable -- Enable logging for a single log channel. memory read -- Read from the memory of the process being debugged. memory write -- Write to the memory of the process being debugged. platform process launch -- Launch a new process on a remote platform. platform select -- Create a platform if needed and select it as the current platform. plugin load -- Import a dylib that implements an LLDB plugin. process launch -- Launch the executable in the debugger. process load -- Load a shared library into the current process. source -- A set of commands for accessing source file information … and so forth …
我們還可以使用help來了解一個命令別名的構成。如:
(lldb) help b … 'b' is an abbreviation for '_regexp-break'
help命令的另一個特性是可以查看某個具體參數的使用,我們以”break command add”命令為例:
(lldb) help break command add Add a set of commands to a breakpoint, to be executed whenever the breakpoint is hit. Syntax: breakpoint command addetc...
如果想了解以上輸出的參數
(lldb) help-- Breakpoint IDs consist major and minor numbers; the major etc...
幫助系統能讓我們快速地了解一個LLDB命令的使用方法。經常使用它,可以讓我們更快地熟悉LLDB的各項功能,所以建議多使用它。
總結
LLDB帶給我們強大的調試功能,在調試過程中充分地利用它可以幫助我們極大地提高調試效率。我們可以不用寫那麼多的NSLog來打印一大堆的日志。所以建議在日常工作中多去使用它。當然,上面的命令只是LLDB的冰山一角,更多的使用還需要大家自己去發掘,在此只是拋磚引玉,做了一些整理。
參考
The LLDB Debugger
LLDB Quick Start Guide
與調試器共舞 – LLDB 的華爾茲
LLDB調試命令初探
NSLog效率低下的原因及嘗試lldb斷點打印Log
- 在uiview 的tableView中點擊cell進入跳轉到另外一個界面的完成辦法
- iOS開辟之UIScrollView控件詳解
- 進修iOS自界說導航掌握器UINavigationController
- iOS 開辟中 NavigationController常常湧現的成績緣由剖析
- iOS簡略登錄LoginViewController、注冊RegisterViewController等功效完成辦法
- iOS自界說collectionView完成毛玻璃後果
- ios開辟navigationController pushViewController 方法屢次跳轉前往到最下層前往到指定的某一層的完成辦法
- iOS獲得cell中webview的內容尺寸
- 處理JSON數據由於null招致數據加載掉敗的辦法
- iOS逆向工程應用LLDB的USB銜接調試第三方App
- UIMenuController在Cell外部沒法顯示的處理方法(iOS9.2)
- iOS中navigationController 去失落配景圖片、去失落底部線條的焦點代碼
- iOS運用中UICollectionViewCell定制Button
- Android中getActivity()為null的處理方法
- iOS 處理UICollectionView 盤算 Cell 年夜小的成績