舉例講解iOS應用開發中hitTest觸摸事件的編寫方法
hitTest:withEvet 調用過程
比如如果是當前的View A, 還有一個viewB
如果不重寫 hitTest 方法,那麼 系統默認是先調用viewA的hitest 方法,然後再調用viewB的htest方法。
系統的調用過程,跟下面的重寫hitest的方法是一模一樣的。
復制代碼 代碼如下:
-(UIView*)hitTest:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
if ([self pointInside:point withEvent:event]) {
}
else {
return nil;
}
for (UIView *subView in self.subviews) {
if ([subView hitTest:point withEvent:event]!=nil) {
return subView;
}
}
return self;
}
在說明一次,如果不重寫hitest方法,那麼每一個UIVIeew的默認hitest的方法都是上面這個處理流程。
那也沒啥好說的。
但是對於一些特殊的處理過程,就不行了
所以之所以重寫hitTest方法,通常都是為了穿透上層 的 UIview,讓touch事件可以達到下面的uiview,
比如 view A 和 VIew B,
View b完全擋住了view A,但是我想讓點擊viewB的時候,view A可以響應點擊的事件。就可以采用下面的方法:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
-(UIView*)hitTest:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
if ([self pointInside:point withEvent:event]) {
NSLog(@"in view A");
return self;
}
else {
return nil;
}
}
深入
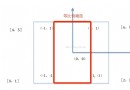
我們來更深入一下,現在有個實例需求界面如下,
Window
-ViewA
-ButtonA
-ViewB
-ButtonB
層次結構:ViewB完全蓋住了ButtonA,ButtonB在ViewB上,現在需要實現:
(1)ButtonA和ButtonB都能響應消息 (2)ViewA也能收到ViewB所收到的touches消息 (3)不讓ViewB(ButtonB)收到消息。
(首先解析下,默認情況下,點擊了ButtonB的區域,iOS消息處理過程。
-ViewA
-ButtonA
-ViewB
-ButtonB
當點擊ButtonB區域後,處理過程:從ViewA開始依次調用hitTest
pointInside的值依次為:
ViewA:NO;
ViewB:YES;
ButtonB:YES;
ButtonB的subViews:NO;
所以ButtonB的subViews的hitTest都返回nil,於是返回的處理對象是ButtonB自己。接下去開始處理touches系列方法,這裡是調用ButtonB綁定的方法。處理完後消息就停止,整個過程結束。)
分析:
實現的方式多種,這裡將兩個需求拆解開來實現,因為實現2就可以滿足1。
需求1的實現,ViewB蓋住了ButtonA,所以默認情況下ButtonA收不到消息,但是在消息機制裡尋找消息響應是從父View開始,所以我們可以在ViewA的hitTest方法裡做判斷,若touch point是在ButtonA上,則將ButtonA作為消息處理對象返回。
代碼如下:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
#pragma mark - hitTest
- (UIView *)hitTest:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
// 當touch point是在_btn上,則hitTest返回_btn
CGPoint btnPointInA = [_btn convertPoint:point fromView:self];
if ([_btn pointInside:btnPointInA withEvent:event]) {
return _btn;
}
// 否則,返回默認處理
return [super hitTest:point withEvent:event];
}
這樣,當觸碰點是在ButtonA上時,則touch消息就被攔截在ViewA上,ViewB就收不到了。然後ButtonA就收到touch消息,會觸發onClick方法。
需求2的實現,上面說到響應鏈,ViewB只要override掉touches系列的方法,然後在自己處理完後,將消息傳遞給下一個響應者(即父View即ViewA)。
代碼如下:在ViewB代碼裡
復制代碼 代碼如下:
#pragma mark - touches
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
NSLog(@"B - touchesBeagan..");
// 把事件傳遞下去給父View或包含他的ViewController
[self.nextResponder touchesBegan:touches withEvent:event];
}
- (void)touchesCancelled:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
NSLog(@"B - touchesCancelled..");
// 把事件傳遞下去給父View或包含他的ViewController
[self.nextResponder touchesBegan:touches withEvent:event];
}
- (void)touchesEnded:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
NSLog(@"B - touchesEnded..");
// 把事件傳遞下去給父View或包含他的ViewController
[self.nextResponder touchesBegan:touches withEvent:event];
}
- (void)touchesMoved:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
NSLog(@"B - touchesMoved..");
// 把事件傳遞下去給父View或包含他的ViewController
[self.nextResponder touchesBegan:touches withEvent:event];
}
然後,在ViewA上就可以接收到touches消息,在ViewA上寫:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
#pragma mark - touches
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
NSLog(@"A - touchesBeagan..");
}
- (void)touchesCancelled:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
NSLog(@"A - touchesCancelled..");
}
- (void)touchesEnded:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
NSLog(@"A - touchesEnded..");
}
- (void)touchesMoved:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
NSLog(@"A - touchesMoved..");
}
這樣就實現了向父View透傳消息。
不讓ViewB收到消息,可以設置ViewB.UserInteractionEnable=NO;除了這樣還可以override掉ViewB的ponitInside,原理參考上面。
在ViewB上寫:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
- (BOOL)pointInside:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
// 本View不響應用戶事件
return NO;
}
- 實例講授iOS中的UIPageViewController翻頁視圖掌握器
- 實例講授iOS中的CATransition轉場動畫應用
- 舉例講授iOS運用開辟中hitTest觸摸事宜的編寫辦法
- 舉例講授設計形式中的原型形式在iOS運用開辟中的感化
- 實例講授iOS運用開辟中UIPickerView轉動選擇欄的用法
- 舉例講授iOS運用開辟中對設計形式中的戰略形式的應用
- 舉例講授Objective-C中@property屬性的用法
- 實例講授設計形式中的敕令形式在iOS App開辟中的應用
- 實例講授若何在iOS運用開辟中應用設計形式中的署理形式
- 實例講授iOS運用的設計形式開辟中的Visitor拜訪者形式
- iOS開辟中完成一個簡略的圖片閱讀器的實例講授
- 實例講授iOS運用開辟中應用UITableView創立自界說表格
- 實例講授iOS運用UI開辟之基本動畫的創立
- 舉例講授iOS開辟中拖動視圖的完成
- 舉例講授iOS中延遲加載和上拉刷新/下拉加載的完成