淺析iOS應用開發中線程間的通信與線程安全問題
線程間的通信
簡單說明
線程間通信:在1個進程中,線程往往不是孤立存在的,多個線程之間需要經常進行通信
線程間通信的體現
1個線程傳遞數據給另1個線程
在1個線程中執行完特定任務後,轉到另1個線程繼續執行任務
線程間通信常用方法
復制代碼 代碼如下:
- (void)performSelectorOnMainThread:(SEL)aSelector withObject:(id)arg waitUntilDone:(BOOL)wait;
- (void)performSelector:(SEL)aSelector onThread:(NSThread *)thr withObject:(id)arg waitUntilDone:(BOOL)wait;
線程間通信示例 – 圖片下載
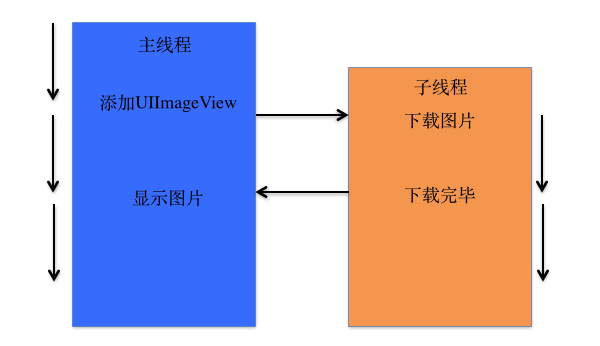
復制代碼 代碼如下:
//
// YYViewController.m
// 06-NSThread04-線程間通信
//
// Created by apple on 14-6-23.
// Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved.
//
#import "YYViewController.h"
@interface YYViewController ()
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIImageView *iconView;
@end
復制代碼 代碼如下:
@implementation YYViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
}
-(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
// 在子線程中調用download方法下載圖片
[self performSelectorInBackground:@selector(download) withObject:nil];
}
-(void)download
{
//1.根據URL下載圖片
//從網絡中下載圖片
NSURL *urlstr=[NSURL URLWithString:@"fdsf"];
//把圖片轉換為二進制的數據
NSData *data=[NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:urlstr];//這一行操作會比較耗時
//把數據轉換成圖片
UIImage *image=[UIImage imageWithData:data];
//2.回到主線程中設置圖片
[self performSelectorOnMainThread:@selector(settingImage:) withObject:image waitUntilDone:NO];
}
//設置顯示圖片
-(void)settingImage:(UIImage *)image
{
self.iconView.image=image;
}
@end
代碼2:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
//
// YYViewController.m
// 06-NSThread04-線程間通信
//
// Created by apple on 14-6-23.
// Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved.
//
#import "YYViewController.h"
#import <NSData.h>
@interface YYViewController ()
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIImageView *iconView;
@end
復制代碼 代碼如下:
@implementation YYViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
}
-(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
// 在子線程中調用download方法下載圖片
[self performSelectorInBackground:@selector(download) withObject:nil];
}
-(void)download
{
//1.根據URL下載圖片
//從網絡中下載圖片
NSURL *urlstr=[NSURL URLWithString:@"fdsf"];
//把圖片轉換為二進制的數據
NSData *data=[NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:urlstr];//這一行操作會比較耗時
//把數據轉換成圖片
UIImage *image=[UIImage imageWithData:data];
//2.回到主線程中設置圖片
//第一種方式
// [self performSelectorOnMainThread:@selector(settingImage:) withObject:image waitUntilDone:NO];
//第二種方式
// [self.imageView performSelector:@selector(setImage:) onThread:[NSThread mainThread] withObject:image waitUntilDone:NO];
//第三種方式
[self.iconView performSelectorOnMainThread:@selector(setImage:) withObject:image waitUntilDone:NO];
}
//設置顯示圖片
//-(void)settingImage:(UIImage *)image
//{
// self.iconView.image=image;
//}
@end
線程安全
一、多線程的安全隱患
資源共享
1塊資源可能會被多個線程共享,也就是多個線程可能會訪問同一塊資源
比如多個線程訪問同一個對象、同一個變量、同一個文件
當多個線程訪問同一塊資源時,很容易引發數據錯亂和數據安全問題
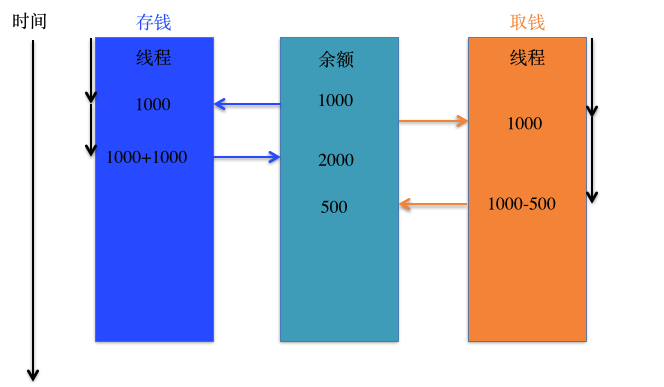
示例一:
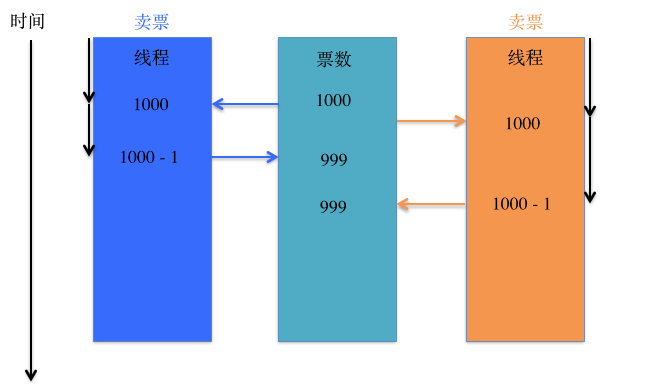
示例二:
問題代碼:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
//
// YYViewController.m
// 05-線程安全
//
// Created by apple on 14-6-23.
// Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved.
//
#import "YYViewController.h"
@interface YYViewController ()
//剩余票數
@property(nonatomic,assign) int leftTicketsCount;
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSThread *thread1;
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSThread *thread2;
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSThread *thread3;
@end
復制代碼 代碼如下:
@implementation YYViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
//默認有20張票
self.leftTicketsCount=10;
//開啟多個線程,模擬售票員售票
self.thread1=[[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(sellTickets) object:nil];
self.thread1.name=@"售票員A";
self.thread2=[[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(sellTickets) object:nil];
self.thread2.name=@"售票員B";
self.thread3=[[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(sellTickets) object:nil];
self.thread3.name=@"售票員C";
}
-(void)sellTickets
{
while (1) {
//1.先檢查票數
int count=self.leftTicketsCount;
if (count>0) {
//暫停一段時間
[NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:0.002];
//2.票數-1
self.leftTicketsCount= count-1;
//獲取當前線程
NSThread *current=[NSThread currentThread];
NSLog(@"%@--賣了一張票,還剩余%d張票",current,self.leftTicketsCount);
}else
{
//退出線程
[NSThread exit];
}
}
}
-(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
//開啟線程
[self.thread1 start];
[self.thread2 start];
[self.thread3 start];
}
@end
打印結果:
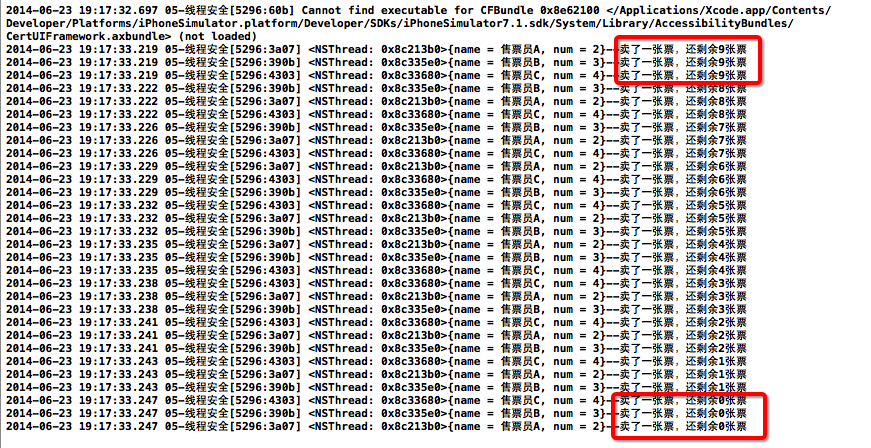
二、安全隱患分析
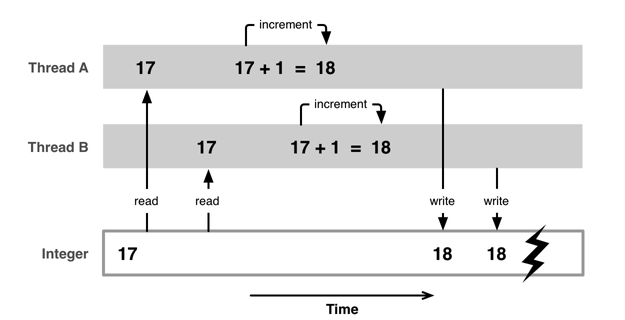
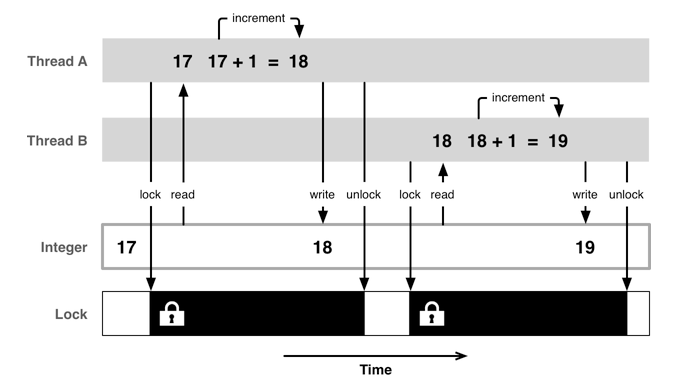
三、如何解決
互斥鎖使用格式
@synchronized(鎖對象) { // 需要鎖定的代碼 }
注意:鎖定1份代碼只用1把鎖,用多把鎖是無效的
代碼示例:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
//
// YYViewController.m
// 05-線程安全
//
// Created by apple on 14-6-23.
// Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved.
//
#import "YYViewController.h"
@interface YYViewController ()
//剩余票數
@property(nonatomic,assign) int leftTicketsCount;
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSThread *thread1;
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSThread *thread2;
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSThread *thread3;
@end
@implementation YYViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
//默認有20張票
self.leftTicketsCount=10;
//開啟多個線程,模擬售票員售票
self.thread1=[[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(sellTickets) object:nil];
self.thread1.name=@"售票員A";
self.thread2=[[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(sellTickets) object:nil];
self.thread2.name=@"售票員B";
self.thread3=[[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(sellTickets) object:nil];
self.thread3.name=@"售票員C";
}
-(void)sellTickets
{
while (1) {
@synchronized(self){//只能加一把鎖
//1.先檢查票數
int count=self.leftTicketsCount;
if (count>0) {
//暫停一段時間
[NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:0.002];
//2.票數-1
self.leftTicketsCount= count-1;
//獲取當前線程
NSThread *current=[NSThread currentThread];
NSLog(@"%@--賣了一張票,還剩余%d張票",current,self.leftTicketsCount);
}else
{
//退出線程
[NSThread exit];
}
}
}
}
-(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
//開啟線程
[self.thread1 start];
[self.thread2 start];
[self.thread3 start];
}
@end
執行效果圖
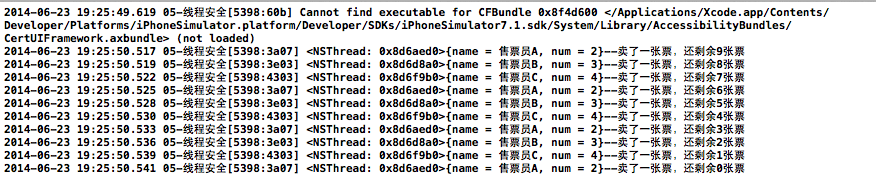
互斥鎖的優缺點
優點:能有效防止因多線程搶奪資源造成的數據安全問題
缺點:需要消耗大量的CPU資源
互斥鎖的使用前提:多條線程搶奪同一塊資源
相關專業術語:線程同步,多條線程按順序地執行任務
互斥鎖,就是使用了線程同步技術
四:原子和非原子屬性
OC在定義屬性時有nonatomic和atomic兩種選擇
atomic:原子屬性,為setter方法加鎖(默認就是atomic)
nonatomic:非原子屬性,不會為setter方法加鎖
atomic加鎖原理
復制代碼 代碼如下:
@property (assign, atomic) int age;
- (void)setAge:(int)age
{
@synchronized(self) {
_age = age;
}
}
原子和非原子屬性的選擇
nonatomic和atomic對比
- atomic:線程安全,需要消耗大量的資源
- nonatomic:非線程安全,適合內存小的移動設備
iOS開發的建議
- 所有屬性都聲明為nonatomic
- 盡量避免多線程搶奪同一塊資源
- 盡量將加鎖、資源搶奪的業務邏輯交給服務器端處理,減小移動客戶端的壓力




