iOS中應用NSURLConnection處置HTTP同步與異步要求
1、引言
在IOS7後,NSURLSession根本取代了NSURLConnection停止收集開辟,在IOS9後,NSURLConnection相干辦法被完整的棄用,IOS體系有向下兼容的特征,雖然NSURLConnection曾經被棄用,但在開辟中,其辦法仍然可以被應用,而且假如須要兼容到很低版本的iOS體系,有時就必需應用NSURLConnection類了。
2、應用NSURLConnection停止同步要求
關於收集要求分為同步和異步兩種,同步是指在要求成果前往之前,法式代碼會卡在要求處,以後的代碼不會被履行,異步是指在發送要求以後,一邊在子線程中吸收前往數據,一邊履行以後的代碼,當前往數據吸收終了後,采取回調的方法告訴主線程做處置。
應用以下辦法停止NSURLConnection的同步要求:
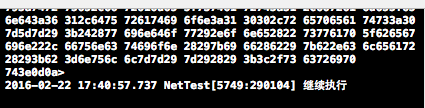
NSURL * url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://www.百度.com"];打印信息以下圖所示,從中可以看出,當數據前往停止時才履行前面的代碼:
NSURLRequest * request = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
NSData * data = [NSURLConnection sendSynchronousRequest:request returningResponse:nil error:nil];
NSLog(@"%@",data);
NSLog(@"持續履行");
3、應用NSURLConnection停止異步要求
應用同步的方法停止要求有一個很年夜的弊病,在停止收集要求時,數據的前往常常須要必定時光,弗成能剎時完成,應用同步的方法將招致界面卡逝世,沒有提醒也不克不及交互任何用戶操作,如許的話,很有能夠會給用戶法式卡逝世的假象。
NSURLConnection類供給兩種方法停止異步要求操作。
1.應用block的方法停止異步要求
應用以下代碼停止block方法的異步要求,在block中會傳入要求到的前往數據和數據信息等參數:
NSURL * url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://www.百度.com"];
NSURLRequest * request = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
//個中的queue參數決議block中的代碼在哪一個隊列中履行
[NSURLConnection sendAsynchronousRequest:request queue:[NSOperationQueue mainQueue] completionHandler:^(NSURLResponse * _Nullable response, NSData * _Nullable data, NSError * _Nullable connectionError) {
NSLog(@"%@",data);
}];
NSLog(@"持續履行");
2.應用署理回調的異步要求方法
起首遵照協定與性命一個可變的NSData用於吸收數據:
@interface ViewController ()<NSURLConnectionDataDelegate>應用以下的代碼停止要求:
{
NSMutableData * _data;
}
@end
_data = [[NSMutableData alloc]init];要求收回後,會一次挪用以下署理辦法停止要求進程的監聽和數據的獲得:
NSURL * url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://www.百度.com"];
NSURLRequest * request = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
[NSURLConnection connectionWithRequest:request delegate:self];
-(void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didReceiveResponse:(NSURLResponse *)response{
//開端吸收數據
[_data setLength:0];
}
-(void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didReceiveData:(NSData *)data{
//正在吸收數據
[_data appendData:data];
}
-(void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didFailWithError:(NSError *)error{
//吸收數據掉敗
NSLog(@"%@",error);
}
-(void)connectionDidFinishLoading:(NSURLConnection *)connection{
//吸收數據完成
NSLog(@"%@",_data);
}
4、示例
1.經由過程NSURLConnection停止異步下載:
NSURLConnection 供給了兩種方法來完成銜接,一種是同步的另外一種是異步的,異步的銜接將會創立一個新的線程,這個線程將會來擔任下載的舉措。而關於同步銜接,鄙人載銜接和處置通信時,則會壅塞以後挪用線程。
很多開辟者都邑以為同步的銜接將會梗塞主線程,其實這類不雅點是毛病的。一個同步的銜接是會壅塞挪用它的線程。假如你在主線程中創立一個同步銜接,沒錯,主線程會壅塞。然則假如你其實不是從主線程開啟的一個同步的銜接,它將會相似異步的銜接一樣。是以這類情形其實不會梗塞你的主線程。現實上,同步和異步的重要差別就是運轉 runtime 為會異步銜接創立一個線程,而同步銜接則不會。
//asynchronousRequest connection
-(void)fetchAppleHtml{
NSString *urlString = @"http://www.apple.com";
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:urlString];
// NSURLRequest *urlRequest = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
NSURLRequest *urlRequest = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url cachePolicy:NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringLocalAndRemoteCacheData timeoutInterval:30.0f]; //maximal timeout is 30s
NSOperationQueue *queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc] init];
[NSURLConnection sendAsynchronousRequest:urlRequest queue:queue completionHandler:^(NSURLResponse *response, NSData *data, NSError *connectionError) {
if ([data length] > 0 && connectionError == nil) {
NSString *documentsDir = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES) objectAtIndex:0];
NSString *filePath = [documentsDir stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"apple.html"];
[data writeToFile:filePath atomically:YES];
NSLog(@"Successfully saved the file to %@",filePath);
NSString *html = [[NSString alloc] initWithData:data encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSLog(@"HTML = %@",html);
}else if ([data length] == 0 && connectionError == nil){
NSLog(@"Nothing was downloaded.");
}else if (connectionError != nil){
NSLog(@"Error happened = %@",connectionError);
}
}];
}
2.經由過程NSURLConnection停止同步下載:
應用 NSURLConnection 的 sendSynchronousRequest:returningResponse:error:類辦法,我們可以停止同步要求。在創立一個同步的收集銜接的時刻我們須要明確一點,其實不是是我們的這個同步銜接必定會梗塞我們的主線程,假如這個同步的銜接是創立在主線程上的,那末這類情形下是會梗塞我們的主線程的,其他的情形下是紛歧定會梗塞我們的主線程的。假如你在 GCD 的全局並發隊列上初始化了一個同步的銜接,你其實其實不會梗塞我們的主線程的。
我們來初始化第一個同步銜接,並看看會產生甚麼。在實例中,我們將測驗考試獲得 Yahoo!美國站點主頁內容:
//synchronousRequest connection
-(void)fetchYahooData{
NSLog(@"We are here...");
NSString *urlString = @"http://www.yahoo.com";
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:urlString];
NSURLRequest *urlRequest = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
NSURLResponse *response = nil;
NSError *error = nil;
NSLog(@"Firing synchronous url connection...");
NSData *data = [NSURLConnection sendSynchronousRequest:urlRequest returningResponse:&response error:&error];
if ([data length] > 0 && error == nil) {
NSLog(@"%lu bytes of data was returned.",(unsigned long)[data length]);
}else if([data length] == 0 && error == nil){
NSLog(@"No data was return.");
}else if (error != nil){
NSLog(@"Error happened = %@",error);
}
NSLog(@"We are done.");
}
/*
|
| as we know, it will chock main thread when we call sendSynchronousRequest on main thread,,,,change below
|
v
*/
//call sendSynchronousRequest on GCD pool
-(void)fetchYahooData2_GCD{
NSLog(@"We are here...");
NSString *urlString = @"http://www.yahoo.com";
NSLog(@"Firing synchronous url connection...");
dispatch_queue_t dispatchQueue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0);
dispatch_async(dispatchQueue, ^{
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:urlString];
NSURLRequest *urlRequest = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
NSURLResponse *response = nil;
NSError *error = nil;
NSData *data = [NSURLConnection sendSynchronousRequest:urlRequest returningResponse:&response error:&error];
if ([data length] > 0 && error == nil) {
NSLog(@"%lu bytes of data was returned.",(unsigned long)[data length]);
}else if ([data length] == 0 && error == nil){
NSLog(@"No data was returned.");
}else if (error != nil){
NSLog(@"Error happened = %@",error);
}
});
NSLog(@"We are done.");
}
檢查運轉輸入成果,分離為:
synchronous download on main thread without GCD
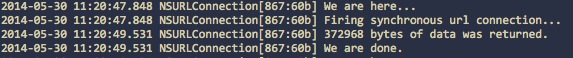
synchronous download on main thread with GCD
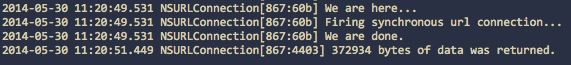
可以看到在主線程上挪用同步下載會壅塞以後線程,而應用GCD則不會。
【iOS中應用NSURLConnection處置HTTP同步與異步要求】的相關資料介紹到這裡,希望對您有所幫助! 提示:不會對讀者因本文所帶來的任何損失負責。如果您支持就請把本站添加至收藏夾哦!